Bank of Central African States (CFA) |
| |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
 |
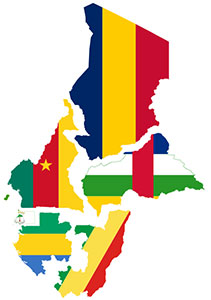
Map of the six Central African States (CFA) and their flags (on the left). |
|
 |
|
 |
Exemple of a CFA 500 Francs banknote, 2000, Republic of the Congo (C). |
|
|
 |
Exemple of a CFA 500 Francs banknote, 2002, Central African Republic (M). |
Member States
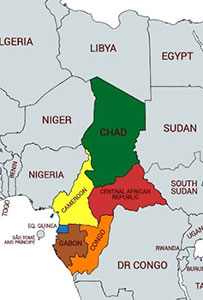
The Central African CFA franc (French: franc CFA or simply franc, ISO 4217 code: XAF) is the currency of six independent states in Central Africa:
Cameroon,
Central African Republic,
Chad,
Republic of the Congo,
Equatorial Guinea
Gabon.
Date of Issue: First two digits of a serial number indicate the last two digits of the year of issue.
Banknotes are issued with a letter:
1994 series:
- C – Congo
- E – Cameroon
- F – Central African Republic
- L – Gabon
- N – Equatorial Guinea
- P – Chad
2002 series:
- A – Gabon
- C – Chad
- F – Equatorial Guinea
- M – Central African Republic
- T – Congo
- U – Cameroon
CFA stands for Coopération financière en Afrique centrale ("Financial Cooperation in Central Africa").
It is issued by the BEAC (Banque des États de l'Afrique Centrale, "Bank of the Central African States"), located in Yaoundé, Cameroon, for the members of the CEMAC (Communauté Économique et Monétaire de l'Afrique Centrale, "Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa").
These six countries have a combined population of 55.2 million people and a combined GDP of US$113.322 billion as of 2020.
The franc is nominally subdivided into 100 centimes but no centime denominations have been issued.
It came into use in 1945, replacing the French Equatorial African franc (which was introduced in 1917) throughout the French colonies in the region.
While formerly pegged to the French franc at a value of 100 CFA francs to 1 French franc, it is currently on a fixed peg with the EUR. The peg is 1 EUR to 655,957 XAF (2021).
|
|






