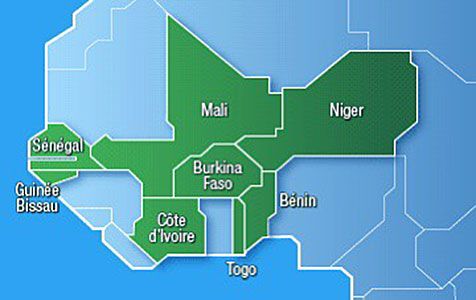
The Central Bank of West African States (French: Banque Centrale des États de l'Afrique de l'Ouest, BCEAO) is a central bank serving the eight west African countries which share the common West African CFA franc currency and comprise the West African Economic and Monetary Union (UEMOA):
- Benin
- Burkina Faso
- Guinea-Bissau
- Ivory Coast (Côte d'Ivoire)
- Mali
- Niger
- Senegal
- Togo
The Bank is active in developing financial inclusion policy and is a member of the Alliance for Financial Inclusion.
Its predecessor, the Institut d’Emission de l’Afrique Occidentale Française et du Togo ("note-issuing institute of French West Africa and Togo"), was created in 1955 and became BCEAO in 1959. The treaty establishing the West African Monetary Union (UMOA), signed on May 12, 1962, gave BCEAO the exclusive right to issue currency as the common central bank for the, then, seven member countries:
- Ivory Coast
- Dahomey (modern day Benin)
- Haute-Volta (modern day Burkina Faso)
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Niger
- Senegal
On June 30, 1962 Mali left the group and adopted the Malian franc as national currency. On December 17, 1963 Togo officially joined the UMOA. On May 30, 1973 Mauritania withdrew and adopted the ouguiya as national currency. On February 17, 1984, Mali re-joined the UMOA.
Symbol
On each coin and on the front of the banknotes is represented the BCEAO logo, a stylized sawfish. This represents a bronze figurine formerly used by the Akan to weigh gold. In their mythology, this species embodies the power of the sea, fertility and prosperity.
CFA stands for Coopération financière en Afrique centrale ("Financial Cooperation in Central Africa").
It is issued by the BEAC (Banque des États de l'Afrique Centrale, "Bank of the Central African States"), located in Yaoundé, Cameroon, for the members of the CEMAC (Communauté Économique et Monétaire de l'Afrique Centrale, "Economic and Monetary Community of Central Africa").
The franc is nominally subdivided into 100 centimes but no centime denominations have been issued.
It came into use in 1945, replacing the French Equatorial African franc (which was introduced in 1917) throughout the French colonies in the region.
While formerly pegged to the French franc at a value of 100 CFA francs to 1 French franc, it is currently on a fixed peg with the EUR. The peg is 1 EUR to 655,957 XAF (2021).
|